Principles of Algorithmic Management

The analysis of algorithmic management will be distorted if understood only as an extension of scientific management in the supervision of labor. In this essay we develop a theory of algorithmic management in relation to fundamental changes in the shape and structure of organization in the 21st Century that are reconfiguring boundaries, roles, and relations among managers, workers, engineers, professionals, consumers, and other user categories. To grasp the distinctive principles of algorithmic management, we compare and contrast the features of its ideology and practices with those of scientific management and the more recent collaborative form of management. Algorithmic management, we argue, operates within a different organizational form, articulates a different ideology, and addresses different managerial problems with different governance principles along different lines of accountability.
David Stark and Pieter Vanden Broeck, “Principles of Algorithmic Management.” Organization Theory 2024, vol 15, no 2.
Download Paper: Principles of Algorithmic Management
From Oklahoma to Algorithmic Management

This is a very wide-ranging interview conducted in Santiago, Chile (Fall 2023) with the editors of Estudios Publicos.
Download English Translation: From Oklahoma to algorithmic management. An Interview with David Stark
Download Original Version: De Oklahoma al management algorítmico. Una entrevista con David Stark
Racial Attention Deficit

Racial minorities bring novel perspectives to the organizations in which they work. But what if White Americans are not paying attention to their Black colleagues? In an experiment involving more than 2,500 White working-age Americans, we show that Whites are less likely to follow the choices and learn from their Black peers. We further propose and test several measures to mitigate this racial attention deficit.
Sheen S. Levine, Charlotte Reypens, and David Stark, “Racial Attention Deficit.” Science Advances 2021, vol 7, no 38. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg9508
Read Paper: Racial Attention Deficit
Observational Learning in Networks of Competition
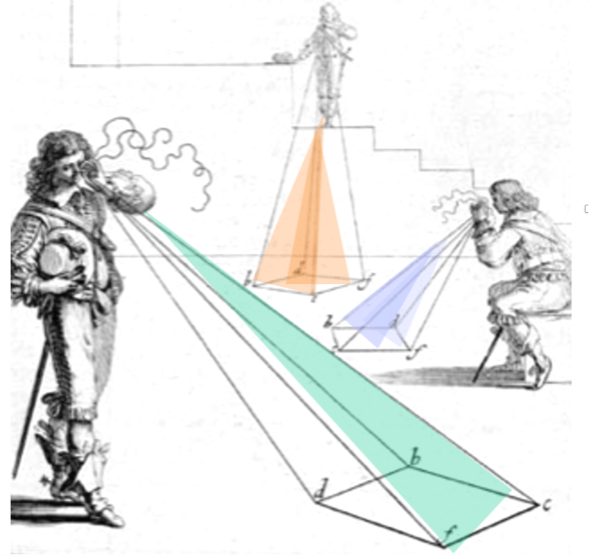
Much of social network analysis has focused on learning in communication networks among collaborators in which actors can make direct inquiries to seek clarification about alters’ behavior or views. But such inquiries are typically not possible among rivals. Learning among rivals occurs primarily in observational networks in which actors must make inferences of the logics guiding their competitors’ behavior in markets. What promotes interpretive advantage in these networks of observation? In network-analytic terms we suggest that competitors’ interpretive advantage lies in non-redundant dyadic closure, especially when dealing with uncertain market niches. Shifting the focus from direct social ties to the cognitive ties that link actors based on the objects, problems, or issues to which they pay attention, we develop a new approach to network analysis. Observation networks, we argue, operate neither as pipes nor as prisms but can be better conceived as scopes.
Matteo Prato and David Stark, “Observational Learning in Networks of Competition: How structures of attention among rivals can bring interpretive advantage.” Organization Studies 2023, vol 44, no 2, pp. 253-276.
Download Paper: Observational Learning in Networks of Competition
Moments of Identity

Ziggy Stardust, Bob Dylan, Deadmou5: What is the relationship between artistic personas, the artists that bear their names, and the audience? In this paper we study persona as a part that stands apart, an object that others can recognize and by which the artist can be recognized. Yet, all the while, what is recognized defies the artist’s complete control. Variously and independently attached to artist and audience, persona fuels a three-way dynamics of identity similar to what we observe everyday with online profiles.
Giovanni Formilan and David Stark. “Moments of Identity: The Dynamics of Artist, Persona, and Audience in Electronic Music.” Theory & Society, vol 52, no 1, pp. 35-64.
Read paper: Moments of Identity
Algorithmic Management in the Platform Economy
The platform model is a new organizational form distinct from markets, hierarchies and networks. This papers shows how platforms co-opt the behavior of providers and users through non-bureaucratic rules, ratings translated into rankings, and twisted feedback loops that deflect accountability. It relates power asymmetries at the organizational level to coalitions at the regulatory level.
Ivana Pais and David Stark, “Algorithmic Management in the Platform Economy.” Sociologica 2020, vol 14, no 3, pp. 47-72.
Download Paper: Algorithmic Management in the Platform Economy
Thematic Issue: Power and Control in Platform Monopoly Capitalism

This thematic Issue of Sociologica is devoted to research on the distinguishing organizational form of the 21st century – the platform model. Focusing on issues of power and control, contributors include: Koray Caliskan, Koen Frenken, Gernot Grabher, Martin Kenney, Ivana Pais, Jamie Peck, Juliet Schor, David Stark, Janet Vertesi, Elizabeth Watkins, and their various co-authors.
Ivana Pais and David Stark, “Power and Control in Platform Monopoly Capitalism.” Sociologica 2020, vol 14, no 3, pp. 43-46.
Download Paper: Power and Control in Platform Monopoly Capitalism
Testing and Being Tested in Pandemic Times
Two types of testing are proliferating during the coronavirus pandemic. The first type is testing – medical tests to diagnosis the virus as well as epidemiological models that project its course. In the second type, actors, organizations, and institutions are being tested in a moment of social and political crisis. This essay analyzes the similarities and differences between these two major types of tests in order to understand their entanglements in the crisis.
David Stark, “Testing and Being Tested in Pandemic Times.” Sociologica 2020, vol 14, no 1, pp. 67-94.
Download Paper: Testing and Being Tested
Put to the Test: For a New Sociology of Testing

Tests have become such a familiar genre that today it seems almost anything can be a test situation. There are stress tests and screen tests, personality tests and citizenship tests, tests of strength and tests of faith. The challenge that a new sociology of testing must address is that ubiquitous testing changes the relations between science, engineering and sociology: It is not that the tests of 21st Century engineering occur within a social context but that it is the very fabric of the social that is being put to the test.
Noortje Marres and David Stark, “Put to the Test: For a New Sociology of Testing.” British Journal of Sociology 2020, vol 71, no 3, pp. 423-443.
Download Paper: Put to the Test
The Performance Complex

What happens when ever more activities in many domains of everyday life are evaluated and experienced in terms of performance metrics? The ratings and rankings of such systems do not have prices but are more like the prizes of competitions. Yet unlike organized competitions, they are ceaseless and without formal entry. Instead of producing resolutions, their scorings create addictions.
In the networks of observation of the performance society all are performing and all keeping score. I refer to this assemblage of metrics, networks, and their attendant emotional pathologies as the performance complex.
David Stark, “The Performance Complex,” introductory chapter for The Performance Complex: Competition and Competitions in Social Life, Oxford University Press 2020, pp. 1-27.
Download Paper: The Performance Complex
Download Chapter 1 & Table of Contents: The Performance Complex: Competition and Competitions in Social Life
Underground Testing: Name-Altering Practices as Probes in Electronic Music

Electronic music artists use aliases as test devices to probe and validate artistic identity in the music scene. You’ve likely heard of pseudonymity and anonymity. Another name-altering practice is polyonymy – some electronic music artists have lots of names. Our study based on field work in Berlin.
Giovanni Formilan and David Stark, “Underground Testing: Personas as Probes in Underground Electronic Music”. British Journal of Sociology 2020, vol 71, no 3, pp. 572-589.
Download Paper: Underground Testing: Name-Altering Practices as Probes in Electronic Music
What’s Observed in a Rating? Rankings as Orientation in the Face of Uncertainty

Elena Esposito and I agree with the criticisms of ratings and rankings as simplistic, obscurantist, inaccurate, and subjective. But why are they becoming such an increasingly influential social form. We argue that they function well enough not because they mirror how things are but because they offer a highly visible reference point to which others are attentive and thereby provide an orientation to navigate uncertainty. The concluding section places the problem of ratings and rankings in a broader historical perspective contrasting the ranked society to the society of rankings. Responding to uncertainty, ratings and rankings perpetuate rather than eliminate anxiety.
Elena Esposito and David Stark, “What’s Observed in a Rating?: Rankings as Orientation in the Face of Uncertainty.” Theory, Culture & Society 2019, vol 36, no 4, pp. 3-26.
Watch Silent Lecture: What’s Observed in a Rating? Rankings as Orientation in the Face of Uncertainty
Download Paper: What’s Observed in a Rating? Rankings as Orientation in the Face of Uncertainty
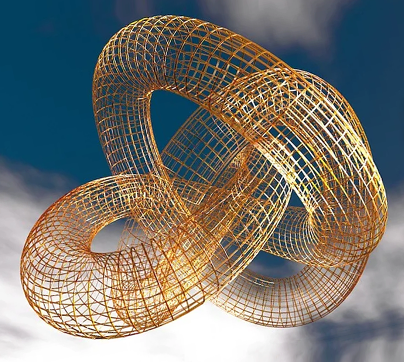
The Möbius Organizational Form: Make, Buy, Cooperate, or Co-opt?

This paper examines the emerging contours of a new organizational form, in which firms move beyond the cooperative pacts of alliances to a radicalized, aggressive co-optation of external assets. Taking our point of departure from the literature on the “networked” firm, we point to an alternative to the make, buy, or cooperate decision: in the Möbius form, firms co-opt resources, unsecured by any alliances, formal or informal. Some companies are brazen in their co-optation, leveraging external assets so thoroughly that they might well be considered a core part of the firm. Enabled by developments in computing technologies, such co-optation challenges traditional models of organizational identity. These fluid boundaries recall the Möbius topological model, which we take as the metaphor for this nascent organizational form. We chart this new behavior by discussing a range of firm activities, including the functions of marketing, research and development, and managerial decision-making, as they are replaced with assets co-opted from other firms in the private sector, government agencies, and lastly the firm’s own users.
David Stark and Elizabeth Watkins, “The Möbius Organizational Form: Make, Buy, Cooperate, or Co-opt?” Sociologica 2018, vol 12, no 1, pp. 65-80.
Download Paper: The Möbius Organizational Form: Make, Buy, Cooperate, or Co-opt?
For What It’s Worth

This essay takes its point of departure from the intellectual milieu in the mid 1980s that gave rise to Luc Boltanski and Laurent Thévenot’s book, On Justification: Economies of Worth. It shows how exposure to ideas and concepts in that book came to take varied forms as they were elaborated and modified in my work across several decades of research in diverse empirical settings. The essay appears in a volume on Economies of Worth and French Pragmatist Sociology edited by Charlotte Cloutier, Jean-Pascal Gond, and Bernard Leca.
David Stark, “For What It’s Worth.” Research in the Sociology of Organizations; Justification, Evaluation and Critique in the Study of Organizations 2017, vol 52, pp. 383-397.
Download Paper: For What It’s Worth
Diversity Makes You Brighter

This essay with co-author Sheen Levine, was published as an OpEd piece in The New York Times, December 9, 2015. On that day, the U.S. Supreme Court heard oral arguments in the affirmative action case of Fisher versus the University of Texas. “Ethnic diversity,” we argue, “is like fresh air: It benefits everybody who experiences it. By disrupting conformity it produces a public good. To step back from the goal of diverse classrooms would deprive all students, regardless of their racial or ethnic background, of the opportunity to benefit from the improved cognitive performance that diversity promotes.”
Sheen Levine and David Stark, “Diversity Makes You Brighter.” The New York Times 2015.
Read Paper: Diversity Makes You Brighter
Pragmatist Perspectives on Valuation: An Introduction

Michael Hutter and I wrote this introductory chapter for an edited volume, Moments of Valuation: Exploring Sites of Dissonance (Oxford University Press, 2015). In making the case for a pragmatist perspective on valuation, we emphasize that valuation takes place in situations. Tastes can be put to test, and these tests are themselves contested. As situations, the contestations over valuation are spatially localized and temporally marked.
Michael Hutter and David Stark, “Pragmatist Perspectives on Valuation: An Introduction.” Moments of Valuation: Exploring Sites of Dissonance. Oxford University Press 2015.
Download Paper: Pragmatist Perspectives on Valuation: An Introduction
Game Changer: The Topology of Creativity

In this paper, Mathijs de Vaan, Balazs Vedres, and I study the social sources of creative success in the video game industry. Teams are most creatively successful when they are composed of overlapping groups that are cognitively heterogeneous.
Mathijs de Vaan, Balazs Vedres, and David Stark, “Game Changer: The Topology of Creativity.” American Journal of Sociology 2015, vol 120, no 4, pp. 1144-1194.
Download Paper: Game Changer: The Topology of Creativity
Download Presentation: Game Changer: The Topology of Creativity
Ethnic Diversity Deflates Price Bubbles

In this paper from the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Sheen Levine and I (together with other co-authors) examine a prominent marekt failure: price bubbles. We propose that bubbles are affected by ethnic homogeneity in the market and can be thwarted by diversity. Using experimental markets in Southeast Asia and North America, we find that market prices fit true values 58% better in ethnically diverse markets. In homogenous markets, overpricing is higher and traders’ errors are more correlated than in diverse markets. The findings suggest that homogeneity promotes conformity. Price bubbles arise not only from individual errors or financial conditions, but also from the social context of decision making. Informing public discussion, our findings suggest that ethnic diversity disrupts conformity and leads to better information processing.
Evan P. Apfelbaum, Valerie L. Bartelt, Mark Bernard, Sheen S. Levine, David Stark, and Edward J. Zajac, “Ethnic Diversity Deflates Price Bubbles.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, vol 111, no 52, pp. 185240-18529.
Download Paper: Ethnic Diversity Deflates Price Bubbles
On Resilience
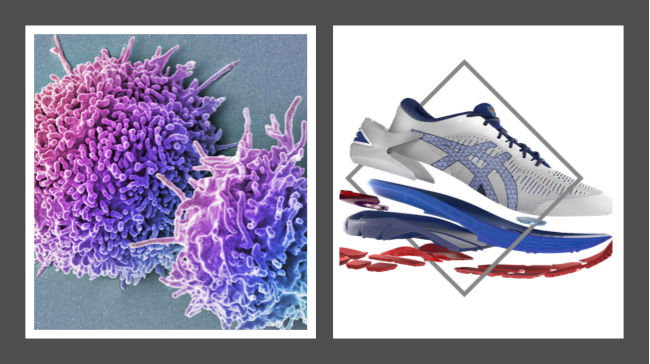
Is resilience more like my sneakers or like my immune system? That is, does resilience in socio-technical systems degrade with use or, like immune systems, is resilience upgraded with use? Similarly, is resilience about responding in the face of the rare event or is it being prepared for the rare event? Is it useful to think about the evolution of resilience?
David Stark, “On Resilience.” Social Sciences 2014, vol 3, no 1, pp. 60-70.
Download Paper: On Resilience
Observing Finance as a Network of Observations

You can observe a lot just by watching,” says Yogi Berra. I use quips by Yogi as a device to organize a commentary on a paper contributing to observation theory by Elena Esposito. The exchange is published in the online journal Sociologica. Yogi’s observation that “The future ain’t what it used to be,” turns out to be a nice summary of Esposito’s analysis of the role of financial models. The second half of the paper is itself a second-order observation. It uses another viewpoint (that of observation theory) to reinterpret my earlier ethnographic and network analytic research on finance.
David Stark, “Observing Finance as a Network of Observations.” Sociologica 2/2013, pp. 1-12.
Download Paper: Observing Finance as a Network of Observations
Attention Networks: A Two-Mode Network View on Valuation

When multiple agents allocate their attention across multiple situations, they create an attention network. In this paper, Matteo Prato and I study how attention networks shape cognition. We argue that how we value something depends on the viewpoints from which we assess it (the background of other objects across which we allocate our attention) and the views of others to which we are differentially exposed because of the network structure of attention. We analyze US financial analysts’ stock coverage portfolios and their estimates of listed firms’ earnings per share from 1993-2011. The study is based on some 10,994,000 analyst-firm observations.
Matteo Prato and David Stark, “Attention Networks: A Two-Mode Network View on Valuation” 2013.
Download Paper: Attention Networks: A Two-Mode Network View on Valuation
Political Holes in the Economy: The Business Network of Partisan Firms in Hungary
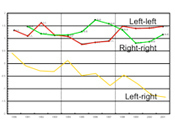
When firms reach out to allies in the political field, the logic of partisanship can constrain the choice of business partners in the economy. Balazs Vedres and I interviewed CEOs and politicians in Hungary and constructed a dataset of all senior managers and boards of directors of the largest 1,696 corporations and the complete set of all political officeholders. Firms of either left or right political affiliation exhibit a preference for partnerships with firms in the same political camp while avoiding ties with firms in the opposite camp. Subsequently, firms with politically balanced boards seize a brokerage opportunity to occupy the political holes in the economy opened up by the growing division between left and right.
David Stark and Balazs Vedres, “Political Holes in the Economy: The Business Network of Partisan Firms in Hungary.” American Sociological Review 2012, vol 77, no 5, pp. 700-722.
Download Paper: Political Holes in the Economy: The Business Network of Partisan Firms in Hungary
Download Presentation: Political Holes in the Economy: The Business Network of Partisan Firms in Hungary
From Dissonance to Resonance: Cognitive Interdependence in Quantitative Finance
How do traders deal with the fallibility of their models? The answer, Daniel Beunza and I show in this ethnographic study of an arbitrage trading room is to use devices for dissonance that disrupt the taken-for-granted and prompt them to reconsider the assumptions built into their databases. Warning: the same socio-technical networks of reflexive modeling that are a source for correction can also lead to the amplification of error.
Daniel Beunza and David Stark, “From Dissonance to Resonance: Cognitive Interdependence in Quantitative Finance.” Economy and Society 2012, vol 41, no 3, pp. 1-35.
Download Paper: From Dissonance to Resonance: Cognitive Interdependence in Quantitative Finance
Download Presentation: From Dissonance to Resonance: Cognitive Interdependence in Quantitative Finance
What’s Valuable?

This essay is the concluding chapter for The Worth of Goods: Valuation and Pricing in the Economy, edited by Patrik Aspers and Jens Beckert (Oxford University Press, 2011). I start with an insight of John Dewey’s that the terms price, prize, and praise all share a common Latin root. To this triplicate I add a fourth, perform, using these four concepts as a device to discuss the papers in the volume. In one section, I address the phenemon of Top Ten lists: On-line ratings and rankings by consumers now provide vast sources of data on prizing and appraising – new means to register value judgments in the economy.
David Stark, “What’s Valuable?” Concluding chapter of The Worth of Goods: Valuation and Pricing in Markets, Patrik Aspers and Jens Beckert, eds. Oxford University Press 2011, pp. 319-338.
Download Paper: What’s Valuable?
Structural Folds: Generative Disruption in Overlapping Groups

What is a social group across time in network terms? This is the key sociological question that Balazs Vedres and I address in this paper. We identify a distinctive network position – the structural fold – at the overlap of cohesive group structures. We show that this structure contributes to creative disruption: groups with structural folds show higher performance but are also more unstable. In the final part of the paper we identify lineages of cohesion: across a longer time frame, groups separate and reunite in an ongoing pattern of interweaving.
Balazs Vedres and David Stark, “Structural Folds: Generative Disruption in Overlapping Groups.” American Journal of Sociology 2010, vol 115, no 4, pp. 1150-90.
Download Paper: Structural Folds: Generative Disruption in Overlapping Groups
Download Presentation: Structural Folds: Generative Disruption in Overlapping Groups
Frequently Asked Questions

In this essay, Gernot Grabher and I play with the genre of Frequently Asked Questions. Keywords: innocence, anticipation, confusion, frustration, resignation, desperation, provocation, hostility.
Gernot Grabher and David Stark, “Frequently Asked Questions.” Environment and Planning A 2009, vol 41 no 2, pp. 255-257.
Download Paper: Frequently Asked Questions
PowerPoint in Public: Digital Technologies and the New Morphology of Demonstration

This paper examines the use of PowerPoint to make demonstrations in the public arena. Our first set of demonstrations are the PowerPoint presentations in December 2002 by the seven finalist architectural teams in the Innovative Design competition for rebuilding the World Trade Center. Our second case occurred some blocks away, several months later: Colin Powell’s PowerPoint demonstration at the United Nations. We argue that Edward Tufte’s denunciation of PowerPoint does not capture the cognitive style made possible by this pervasive new technology.
David Stark and Verena Paravel, “PowerPoint in Public: Digital Technologies and the New Morphology of Demonstration.” Theory, Culture & Society 2008, vol 25, no 5, pp. 31-56.
Download Paper: PowerPoint in Public: Digital Technologies and the New Morphology of Demonstration
Download Presentation: PowerPoint in Public: Digital Technologies and the New Morphology of Demonstration
Socio-technologies of Assembly: Sense-making and Demonstration in Rebuilding Lower Manhattan

Drawing on Science and Technology Studies, Monique Girard and I propose that forms of public assemby vary as distinct combinations of social networks, technologies, and protocols. The key technologies of a public hearing, for example, are a microphone and a stopwatch, combined with rules for who can speak and for how long.
Monique Girard and David Stark, “Socio-technologies of Assembly: Sense-making and Demonstration in Rebuilding Lower Manhattan.” In David Lazer and Viktor Mayer-Schoenberger, eds., Governance and Information: The Rewiring of Governing and Deliberation in the 21st Century. Oxford University Press 2007, pp. 145-76.
Download Paper: Socio-technologies of Assembly: Sense-making and Demonstration in Rebuilding Lower Manhattan
Social Times of Network Spaces: Network Sequences and Foreign Investment in Hungary
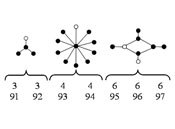
In this paper, Balazs Vedres and I develop a social sequence analysis to identify distinctive pathways whereby firms use network resources to buffer uncertainty, hide or restructure assets, or gain knowledge and legitimacy. In place of properties of the global network, we focus on variation in local properties. In place of a single system time, we model the processes of social times. Our contribution to a more historical network analysis does not simply include time as a variable but, instead, recognizes time as variable.
David Stark and Balazs Vedres, “Social Times of Network Spaces: Network Sequences and Foreign Investment in Hungary.” American Journal of Sociology 2006, vol 111, no 5, pp. 1367-1411.
Download Paper: Social Times of Network Spaces: Network Sequences and Foreign Investment in Hungary
Download Presentation: Social Times of Network Spaces: Network Sequences and Foreign Investment in Hungary
Rooted Transnational Publics: Integrating Foreign Ties and Civic Activism
In the literature on globalization there is a widespread belief that civic associations with transnational ties are uprooted from their domestic societies. Laszlo Bruszt, Balazs Vedres, and I contend that there is not a forced choice between foreign ties and domestic integration. In fact, we find that transnational organizations are more domestically integrated than those without such ties. We base our argument on a survey of 1,002 of the largest civic organizations which we conducted in Hungary. We specify several forms of domestic integration and several forms of transnational ties. By demonstrating a systematic relationship between the patterns of foreign ties and the patterns of domestic integration, we chart three emerging forms of transnational publics.
Laszlo Bruszt, David Stark, and Balazs Vedres, “Rooted Transnational Publics: Integrating Foreign Ties and Civic Activism.” Theory and Society 2006, vol 35, no 3, pp. 323-349.
Download Paper: Rooted Transnational Publics: Integrating Foreign Ties and Civic Activism
Download Presentation: Rooted Transnational Publics: Integrating Foreign Ties and Civic Activism
Resolving Identities: Successive Crises in a Trading Room after 9/11

How do organizations cope with extraordinary crisis? In the second paper about the experiences of our Wall Street traders after September 11th, Daniel Beunza and I report on the process whereby they returned to their restored trading room in the World Financial Center. The trading room did not face one crisis – the immediate aftermath of September 11th – but many: anxiety about additional attacks, questions of professional identity, doubts about the future of the firm, and ambiguities about the future re-location of the trading room. A given crisis was resolved by restoring identities; but identities, once restored, redefined the situation and lead to new crises. That is, the successive waves of crisis were produced by each success in managing crisis.
Daniel Beunza and David Stark, “Resolving Identities: Successive Crises in a Trading Room after 9/11.” In Nancy Foner, Wounded City: The Social Impact of 9/11. Russell Sage Foundation Press 2005, pp. 293-320.
Download Paper: Resolving Identities: Successive Crises in a Trading Room after 9/11
Tools of the Trade: The Socio-Technology of Arbitrage in a Wall Street Trading Room
In this ethnography of a Wall Street derivatives trading room we argue that arbitrage involves an art of association – the construction of comparability across different assets. In place of essential or relational characteristics, the peculiar valuation that takes place in arbitrage is based on an operation that makes something the measure of something else – associating securities to each other. The process of recognizing opportunities and the practices of making novel associations are shaped by the specific socio-spatial and socio-technical configurations of the trading room. Calculation is distributed across persons and instruments as the trading room organizes interaction among diverse principles of valuation.
Daniel Beunza and David Stark, “Tools of the Trade: The Socio-Technology of Arbitrage in a Wall Street Trading Room.” Industrial and Corporate Change 2004, vol 13, no 1, pp. 369-401.
Download Paper: Tools of the Trade
Permanently Beta

Researchers in science and technology studies have long-recognized that the design process is not completed when manufacturers ship out a new product. Instead, users complete the design process when they resist some uses inscribed in the product, identify other affordances, and modify the product. All products, and especially new and unfamiliar ones, entail considerable interpretive flexibility. The new user innovation communities make this insight a part of corporate strategy. Instead of a hit or miss approach, they actively foster communities of users and involve their participation at ever-earlier stages of the design process. This is search when you don’t know what you’re looking for, relying on the users to recognize it when they find it.
Gina Neff and David Stark, “Permanently Beta: Responsive Organization in the Internet Era.” In Philip E. N. Howard and Steve Jones, eds., Society Online: The Internet In Context. Sage 2003, pp. 173-88.
Download Paper: Permanently Beta
The Organization of Responsiveness: Innovation and Recovery in the Trading Rooms of Lower Manhattan

The September 11th attack on the World Trade Center destroyed the trading room where Daniel Beunza and I had been conducting ethnographic research. The traders invited us to witness their recovery, and so Daniel was with them already during the first week after they resumed trading on September 17th. This paper reports on our observations in their makeshift trading room in New Jersey. The breakdown of technology, we argue, is society made visible.
David Beunza and David Stark, “The Organization of Responsiveness: Innovation and Recovery in the Trading Rooms of Lower Manhattan.” Socio-Economic Review 2003, vol 1, no 2, pp. 135-164.
Download Paper: The Organization of Responsiveness: Innovation and Recovery in the Trading Rooms of Lower Manhattan
Crisis, Recovery, Innovation: Responsive Organization after September 11

On December 5, 2001, Columbia’s Center on Organizational Innovation organized a roundtable discussion with senior executives and contingency planning specialists from key World Trade Center firms. This paper with John Kelly reports on that meeting and other interviews that our research team conducted in the early weeks after 9/11. It documents the importance of strong personal ties, lateral self-organization, and nonhierarchical relations in the recovery process. As a response to uncertainty, organizational factors that explain recovery are similar to those that generate innovation.
John Kelly and David Stark, “Crisis, Recovery, Innovation: Responsive Organization after September 11th.” Environment and Planning A 2002, vol 34, no 9, pp. 1523-33.
Download Paper: Crisis, Recovery, Innovation: Responsive Organization after September 11
One Way or Multiple Paths? For a Comparative Sociology of East European Capitalism

This essay, written with my frequent co-author, Laszlo Bruszt, was published in The American Journal of Sociology (January 2001) as part of a very lively debate with Michael Burawoy.
Laszlo Bruszt and David Stark, “One Way or Multiple Paths? For a Comparative Sociology of East European Capitalism.” American Journal of Sociology 2001, vol 106, no 4, pp. 1129-1137.
Download Paper: One Way or Multiple Paths? For a Comparative Sociology of East European Capitalism
Recombinant Property in East European Capitalism

Some years ago, when they were little kids, my children invented a hybrid game. Having left the houses and hotels of their Monopoly set at a friend’s house, they started to use Lego building blocks (much preferred to the Monopoly pieces even after returned) to construct ever more elaborate structures in a game whose rules evolved away from bankrupting one’s opponents and toward attracting customers to the plastic skyscrapers that towered over the Monopoly plain. This strikes me as a good metaphor for innovation and the process of social change. East European capitalism was not built on the ruins of communism but with the ruins of communism.
David Stark, “Recombinant Property in East European Capitalism.” American Journal of Sociology 1996, vol 101, no 4, pp. 993-1027.
Download Paper: Recombinant Property in East European Capitalism